Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) in Java is an important concept which includes core principles of Java such as inheritance , encapsulation , Polymorphism , Abstraction etc along with Classes & Objects which provides a structured approach to build a reusable and maintainable software application.
Before Object-oriented Programming ( OOPS) , Procedural approach was used to build a software application where programmer used to write step-by-step functions which made it harder to manage and reuse code in the large applications.
To overcome these limitations , Object-oriented Programming was introduced .
Key Featnures of OOP in Java:
- OOPS concept keeps related data and methods together which is known as Encapsulation
- OOPS in Java structures the code into logical units using classes and objects
- OOPS concept make the Java code modular , reusable and scalable
- Java OOPS prevents unauthorized access to data
- OOPs concept provides very important concepts such inheritance , encapsulation , polymorphism , abstraction etc .
Characteristics of an OOP (Object Oriented Programming )
- Class
A class in Java is a user-defined prototype or blueprint from which objects are created . Java class can contains fields , methods ,constructors , nested classes , interfaces , functions etc. Class represents the set of properties or methods that are common to all objects of one type . Using Java class , one can create multiple objects with the same behavior instead of writing their code multiple times .
Class declaration include following components :
- Modifiers : A class can be public or can have default access modifier
- Class Name : Java class name should begin with the initial letter capitalized by naming convention.
- Body : The Java class body is surrounded by braces { } .
Basic Java Class Syntax :
[Access_Modifier ] class ClassName {
// Class body: fields , methods , constructors etc .
}
Example :
public class World{
public static void main (String args [] ) {
System.out.println(” This world is Beautiful “);
}
}
2 . Object :
In Java , object is an instance of a class . An object is a basic unit of Object -Oriented Programming that represents real-life entities . Object is a physical entity, whereas class is a logical entity .
An object mainly consist of :
- State : State of an object represents the data or properties of an object, which are stored in fields or variables . For example , Dress object might have a color ( e.g. , pink ) and category(e.g. college uniform ). So here , color red and category college uniform are states of object Dress.
- Behavior : Behavior represents the actions an object can perform . A Dress objects behavior may include wear( ) or stich ()
- Identity : It is a unique name given to an object that enables it to interact with other objects .
- Method : A method is a collection of statements that perform some specific task and return the result to the caller .
Example :
public class Gift {
//Instance variables
private int score;
private String gift ;
// Constructor
public Gift ( int score , String gift ) {
this. score= score ;
this.gift = gift ;
}
// getters method
public int getScore () {
return score ;
}
public String getGift () {
return gift ;
}
// setters method
public void setScore ( int score ) {
this.score =score ;
}
public void setGift ( String gift ) {
this.gift =gift ;
}
//Instance method
public void displayDetails () {
System.out.println(“Score is :”+score);
System.out.println(“Gift is :”+gift);
}
public static void main (String args [] ) {
Gift gif = new Gift ( 95, “$500”);
gif.displayDetails();
}
}
OUTPUT :
score : 95
gift : $500
3.Encapsulation:
Encapsulation in Java is a mechanism of wrapping the code and data together into a single unit.
Key Characteristics of Encapsulation in Java:
- Encapsulated class can hide the implementation details and discloses only the functionality to the user. By making class data and methods private , representation or implementations can later be changed without impacting the class code.
- Encapsulation helps in better maintainability, readability and usability. Encapsulation also helps in data integrity .
Implementation of Encapsulation in Java:
- Declare data as private : By declaring class data as private , hide the class data so that it cannot be accessed directly from outside the class.
- Use getters and setters : Keep the variables private and provide public getter and setter methods for safe modification and for controlled access with validation.
- Use Proper Access Modifiers : Use private access modifier for data hiding and public for methods that provide access.
Example :
class Gift {
//Declare the variable as private
private String giftName;
//Getter method used to get the data
public String getGiftname() {
return giftName;
}
// Setter method is used to set or modify the data
public void setGiftname (String giftName ) {
this.giftName=giftName;
}
}
public class EncapsulationDemo{
public static void main (String args [] ) {
Gift gif = new Gift ();
gif.setGiftname(” $ 1000″ );
System.out.println(“Gift Name : “ +gif.getGiftname());
}
}
OUTPUT :
Gift Name : $1000
Advantages of Encapsulation :
The advantages of Encapsulation are as follows :
- Data Hiding : Encapsulation protects sensitive data from unauthorized access by resticting direct access to class variables .
- Enhanced Security : Encapsulation allows control and validation over data , preventing invalid or harmful values from being set.
- Improved Maintainability : In Encapsulation , changes to internal implementation can be made without affecting external code that uses the class
- Code Reusability : Encapsulated classes can be reused in different programs without changing the internal logic.
- Modularity: Encapsulation promotes organized , modular code by keeping data and methods together within a class.
Disadvantages of Encapsulation:
- Performance Issue: By accessing data through methods instead of directly accessing can introduce a minor performance cost , espicially in critical application.
- Increased Code Complexity : In encapsulation, by writting getter and setter methods for every variable can make the code more longer and complex.
- Less Flexibility: By restricting access to class members may affect the ability of other classes to extend or use the encapsulated class efficiently.
4. Inheritance :
Inheritance in Java is a fundamental principal in OOP ( Object-Oriented Programming ) by which one class is allowed to inherit the properties (fields) and behaviors (methods ) of another class .
A class that inherits the another class can reuse the properties of that class .
Example :
//Parent class
class Gift {
void gifName() {
System.out.println(“Gift is awesome”);
}
}
//Child class
class Studentgift extends Gift {
void giftName () {
System.out.println(“Gift is incredible book “);
}
}
//Child class
class Teachergift extends Gift {
void giftName() {
System.out.println(“Gift is $11000”);
}
}
//Main class
public class InheritanceDemo {
public static void main (String args[] ) {
Gift gif ;
gif = new Studentgift();
gif.giftName();
gif = new Teachergift();
gif.giftName();
}
}
OUTPUT:
Gift is incredible book
Gift is $11000
Advantages of Inheritance in Java :
- Reusability of Code : The code written in parent class(super class ) is common to all subclasses . Child classes ( Sub classes ) can directly use the parent class code .
- Method Overriding : Method overriding is achieved by only inheritance . Method overriding is one of the ways by which Java achieves Run Time Polymorphism.
- Abstraction : Abstraction is a process where implementation details are hidden and only shows the functionality to the user . This concept of abstraction is achieved through inheritance .
HOW INHERITANCE WORKS IN JAVA ?
For inheritance concept, extends keyword is used in Java . This extends keyword enables the subclass to inherit the properties of superclass . When a class extends another class , it inherits the properties of the superclass . When a class extends another class , it means it inherits all the non-primitive members of the superclass . The subclass can also override the methods of superclass or can add new functionality to them .
5. POLYMORPHISM :
Polymorphism in java is one of the important concept which allows objects to behave differently based on their specific class type . In Java , polymorphism allows the same object or method to behave differently based on the context of the project.
Features of Polymorphism:
- Runtime Decision : Java determines which method to call depending on the objects actual class at Runtime .
- Multiple Behaviors: In Java Polymorphism , the same method can behave differently depending on the object .
- Method Overriding : A subclass/childclass can redefine a method of its superclass/parentclass by overriding the method of its parent class .
- Method Overloading : In Java, we can define multiple methods with same name but with different parameters which is called method overloading.
Why to use Polymorphism In Java?
Polymophism in Java has many advantages which are listed below :
- Code Reusability : Polymorphism allows the same class or method to use with different types of objects , which makes the code more reusable .
- Dynamic Behavior : In Java , with polymorphism , Java can select the appropriate method to call at runtime , which gives the program dynamic behavior based on the actual object type rather than the reference type , due to which the flexibility of the program increases .
- Flexibility : Java Polymorphism enables the object of the classes to be treated as objects of a common superclass , which provides flexibility in method execution and object interaction .
- Abstraction : Java Polymorphism allows the use of abstract classes or interfaces , enabling us to work with superclass or interface which simplifies the interaction with objects .
TYPES OF JAVA POLYMORPHISM :
In Java , polymorphism is mainly divided into two types .
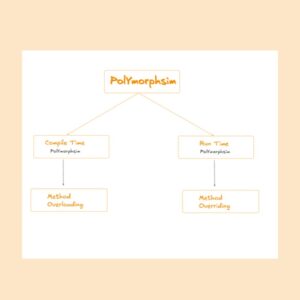
- Compile-Time Polymorphism : Method Overloading in Java is known as Compile-Time polymorphism. Compile-Time Polymorphism is also known as static binding or early binding. Method overloading happens when multiple methods in the same class have the same name but with different parameters .
Method Overloading :
Method overloading in Java means when there are multiple methods with same name but with different parameters . The number of arguments can be different in different method or types of arguments can be different in method overloading . But only change in return types cannot make the method overload as ambiguity problem may occur .
Example :
class Addition
{
int add ( int a , int b )
{
int sum= a+b;
return sum ;
}
int add ( int a , int b , int c )
{
int sum = a+b+c;
return sum;
}
}
class MethodoverloadingExample
{
public static void main (String args [] ) {
Addition aobj=new Addition () ;
System.out.println(aobj.add(34,28));
System.out.println(aobj.add(29,35,1));
}
}
OUTPUT :
62
65
2. Runtime Polymorphism:
Runtime polymorphism in Java is also known as Dynamic Method Dispatch or Late Binding . Java Runtime polymorphism is a process in which a function call to the overriden method is resolved at Runtime . This Runtime polymorphism is achieved through Method overriding .
Method Overriding
In Java, Method Overriding means when a subclass method provides a specific implementation of a method which is already present in its superclass. The overriding method in the subclass must have the same name , return type , and parameters as that of the superclass . Method overriding in Java allows a subclass to extend or modify the behavior of an existing method of the super class . Method overriding enables dynamic method dispatch , where the method that gets executed is determined at runtime .
Example:
// Parent class
class Gift {
//Method in the parent class
public void gift ( ) {
System.out.println(“Gift is awesome “);
}
}
//Child class that inherits from superclass Gift
class StudentGift extends Gift
{
@Override
public void gift() {
System.out.println(“Student Gift is an incredible book”);
}
}
//Child class that inherits from superclass
class TeacherGift extends Gift
{
@Override
public void gift () {
System.out.println(“Teachers gift is $11000”);
}
}
//Main class
public class MethodoverridingDemo{
public static void main (String args [] ) {
// create a Gift object
Gift gif = new Gift () ;
gif. gift(); //calls the Gift class method
//create a TeacherGift object
TeacherGift tgif =new TeacgerGift();
tgif.gift(); // calls the overriden method of TeacherGift class
//Achieve Dynamic Dispatch or Runtime polymorphism
Gift dgif= new StudentGift();
dgif.gift(); // calls the overriden method in StudentGift class
OUTPUT:
Gift is awesome
Teachers gift is $11000
Student gift is an incredible book
6. Abstraction:
Abstraction in java is a core principle of Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) language which is used to hide the internal complex implementation details and show only the necessary functionality & features to the user .
Java Abstraction focuses on what an object does rather than how it does it which siplifies the code organization & simplify the application system.
Some Key Characteristics of Java Abstraction:
- Java Abstraction hides the complex internal implementation details and shows only essential functionality to the user .
- The abstract method present in the abstract class must be implemented by subclass.
- Abstract class can contain both abstract and non abstract method . Abstract method of abstract class must be implemented by subclass.
- Java abstraction define common blueprints , which allows developers to reuse shared behavior across different unrelated classes.
- Abstraction restricts unauthorized access to data by hiding internal implementation details .
How to achieve Abstraction in Java?
In Java, Abstraction can be achieved in two mechanisms : abstract classes and interfaces.
- Abstract Classes :
Abstract class in Java is a class which cannot be instantiated and can contain both abstract & non abstract methods .
Real life example of Java Abstraction:
Sending Message By Android Phone : When you use android phone and send message to another person you just type the message and send , but you don’t know the internal implementation of android messaging. This is real life example of abstraction as internal implementation is hidden showing only functionality to the user .
The Television Remote control : The television remote control is the best example of Java Abstraction . You don’t need to know how the TV internally works ; you just need to press the button to change the channel .
Example:
abstract class Mobilephone{
abstract void calling();
abstract void messaging();
void internet();
}
class Test extends Mobilephone {
//You must override the abstract method of abstract class in subclass
@Override
void calling() {
System.out.println(“Phone calling in Test “);
}
@Override
void messaging () {
System.out.println(“Phone messaging in Test “);
}
}
class DemoAbstractclass {
public static void main ( String args[] ) {
Mobilephone m1 = new Test () ;
m1.calling();
m1.messaging();
}
}
2. Interfaces :
Interface in Java is a blueprint of a class which is used to achieve 100% abstraction in Java.
One interface can extend one or more interface.
One class can implement one or more interface.
Java Interface Syntax :
[access_modifier] interface InterfaceName {
//Contant fields
//Abstract methods
// Default methods (Java 8+ )
// Static methods (Java 8+ )
// Private methods (Java 9+ )
}
Members of an Interface :
Interfaces can contain various memers which are given below :
Constant Fields : All variables (fields ) declared in java interface are implicitly public , static and final which must be initialized at the time of declaration .
Example:
int count=8;
public static final int count =8;
//In the above example both statement are equivalent i.e. in interface by default all fields are public, static and final.
Java Abstract Methods : Before Java 8 , interface could have only abstract methods . These methods are implicitly public and abstract which have no body .
Example :
void calculation ( int count ) ;
public abstract void calculation ( int count ) ;
//In the above example both statement are equivalent i.e. in Java interface by default all methods are public abstract.
Java Static Methods ( Java 8+ ) : From Java 8 , Inteface can have static methods also which can be called using interface name and they are implicitly public .
Example :
static void details () {
System.out.println(” This is an interface static method “);
}
Java Private Methods (Java 9+ ) : Java private methods can be used to share common code between default and static methods within the interface itself , but cannot be accessed by subclasses.
Example :
private void calculation ( ) {
System.out.println(“Calculation done”);
}
Java Interface Example :
interface Calculation {
//abstract method to calculate
double calculate () ;
}
//Implement the Interface in a class name Addition
class Addition implements Calculation {
double a;
double b;
//Constructor for Addition
public Addition(double a , double b ){
this.a=a;
this.b=b;
}
// implementing the abstract method of interface Calculation
public double calculate ( ) {
double sum= a+b;
return sum ;
}
}
class Multiply implements Calculation{
double c;
double d;
//Constructor for multiplication
public Multiply ( double c , double d ) {
this.c=c;
this.d=d;
}
// implementing the abstract method of interface Calculation
public double calculate () {
double mult = c * d ;
return mult ;
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main (String args [] ) {
//Reference type of the object is interface Calculation .
Calculation sum = new Addition (28.0,34.0);
Calculation mult = new Multiply(8.0 , 18.0 ) ;
System.out.println(“Calculated sum is : “ + sum.calculate( ));
System.out.println(” Calculated multiplied value is : “ + mult.calculate());
}
}
OUTPUT :
Calculated sum is : 62.0
Calculated multiplied value is : 144.0
