What is JVM?
Java Virtual Machine (JVM) is a most important component of the Java platform, which act as a Virtual Machine that enables the execution of java bytecode. The JVM act as an interpreter between the java programming language and underlying hardware. It provides a runtime environment for java applications to run on different platforms and operating systems.
When we run Java program , Java compiler first compiles our Java code to bytecode . Then the JVM translate the bytecode into native machine code.
Java is a platform-independent language because of the bytecode as JVM executes the Java bytecode which is platform-independent.
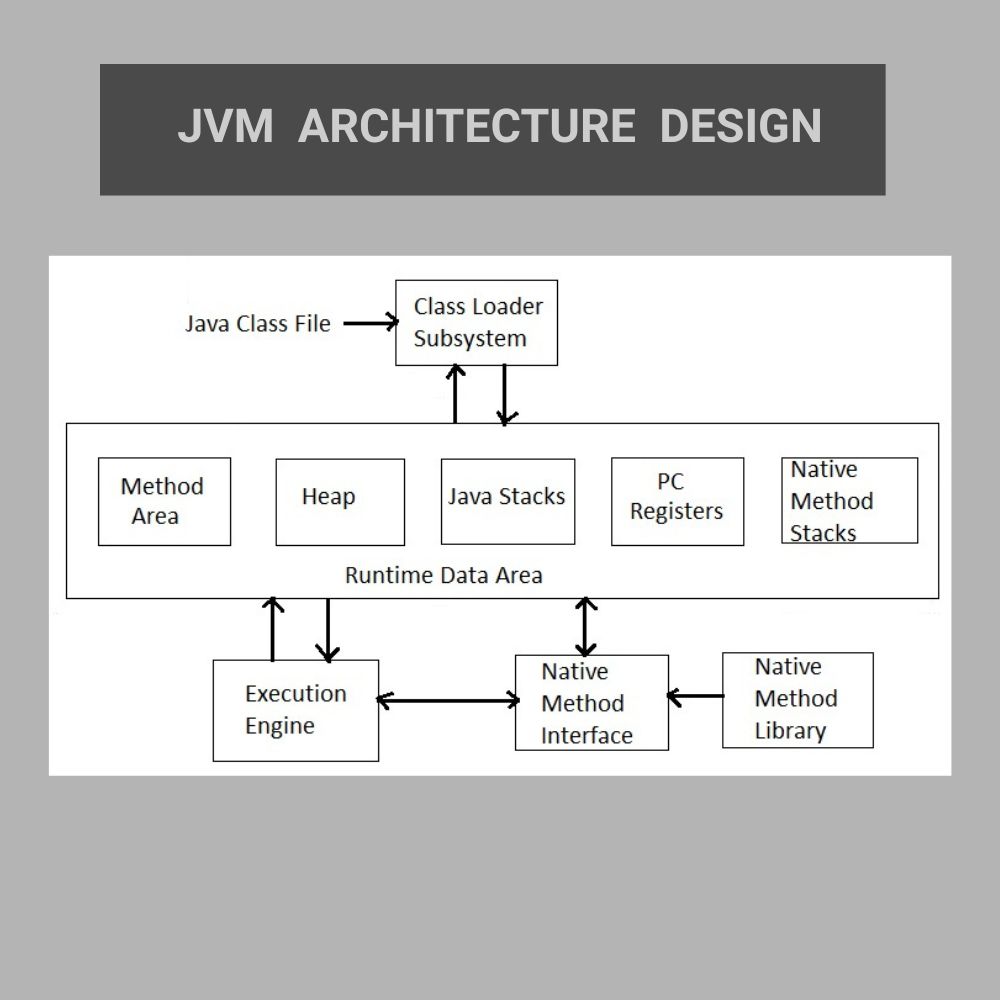
Java Virtual Machine Architecture :
Java virtual machine architecture is divided into three main components :
- Class Loader Subsystem :
- Loading : This Loading component is responsible for loading .class files from the network or file system into memory . There are 3 types of built-in class loaders which are Bootstrap , Extension and Application .
- Linking : This Linking component involves three substeps:
* Verification : Ensures the loaded bytecode is valid and adheres to the JVM specification .
* Preparation : This preparation step allocates memory for static variables and initialise them with default values.
*Resolution : This Resolution step replaces symbolic references in the bytecode with direct references in the Method Area .
- Initialization : Initialization component is responsible for executing the static initializers and static blocks of the class .
2. Runtime Data Areas : These are the memory areas allocated by the JVM during program execution .
- Method Area : This Method Area stores class-level data including the runtime constant pool , field data , method data and the code for methods and constructors . This method area is shared among all threads .
- Heap : Heap memory is a memory where all arrays and objects are allocated . This heap memory is also shared among all threads . The garbage collector primarily operates on the Heap memory .
- JVM Stack : JVM Stack stores local variables , partial results and data for method calls and returns . Each method call creates a new stack frame on the stack . Each thread in the JVM has its own private JVM Stack .
- PC Registers : Each thread has its own PC Register (Program Counter Register ) which stores the address of the next instruction to be executed .
- Native Method Stack : These are used to support native methods which are written in other languages other than Java , C/C++ that are invoked by Java code .
Execution Engine : This Execution Engine component is responsible for executing the bytecode loaded by the Class Loader .
- Interpreter : Interpreter reads and executes bytecode instructions line by line .
- Just-In-Time (JIT ) compiler : JIT compiler improves the performance by compiling frequently executed bytecode segments into native machine code during runtime . This native code can be executed directly by the underlying operating system .
- Garbage Collector : Garbage Collector automatically reclaims memory occupied by the objects that are no longer referenced by the running program which prevents the memory leaks and manage the heap memory efficiency .
What is JRE ?
The JRE ( Java Runtime Environment ) is a software package that provides the necessary components to run the Java applications . The components provided by JRE are Java -class libraries , Java Virtual Machine(JVM ) and other supporting files . JRE is the underlying technology that communicates between the Java program and the operating system .
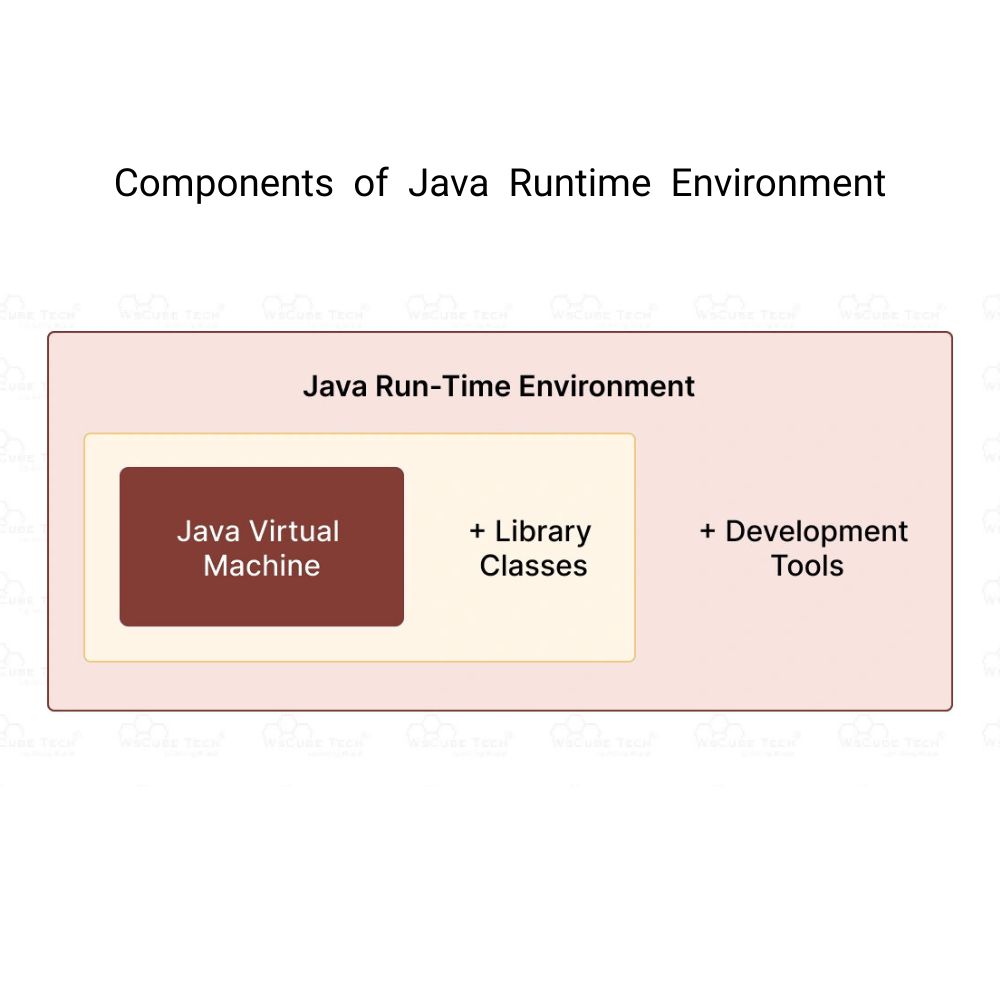
If you don’t want to develop Java application, but only want to run java programs, then you need JRE (Java Runtime Environment )
What is JDK ?
A Java Development Kit (JDK ) is a software package containing the tools developers need to build and run java application .JDK contains different components such as javac to convert source code into byte code , Java Virtual Machine (JVM) , Java Runtime Environment ( JRE ) , development tools and libraries .
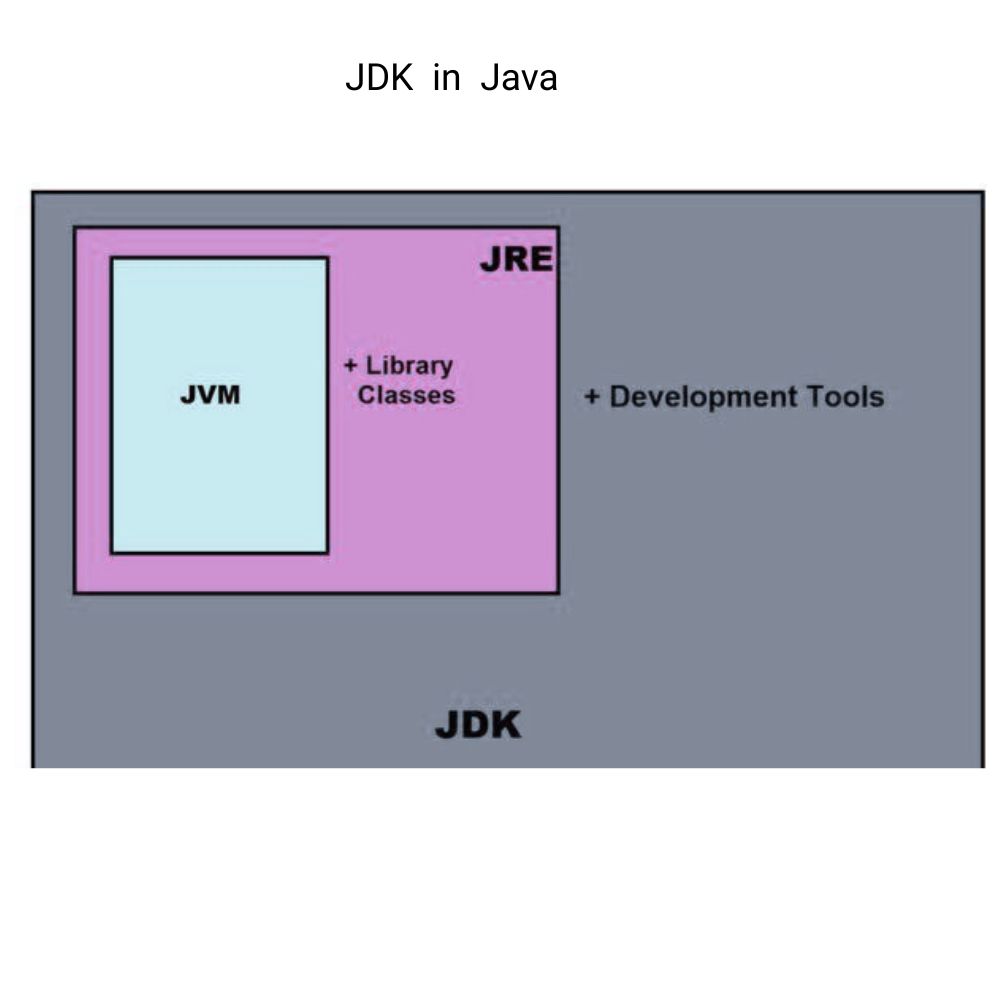
Relationship between JVM , JRE and JDK .
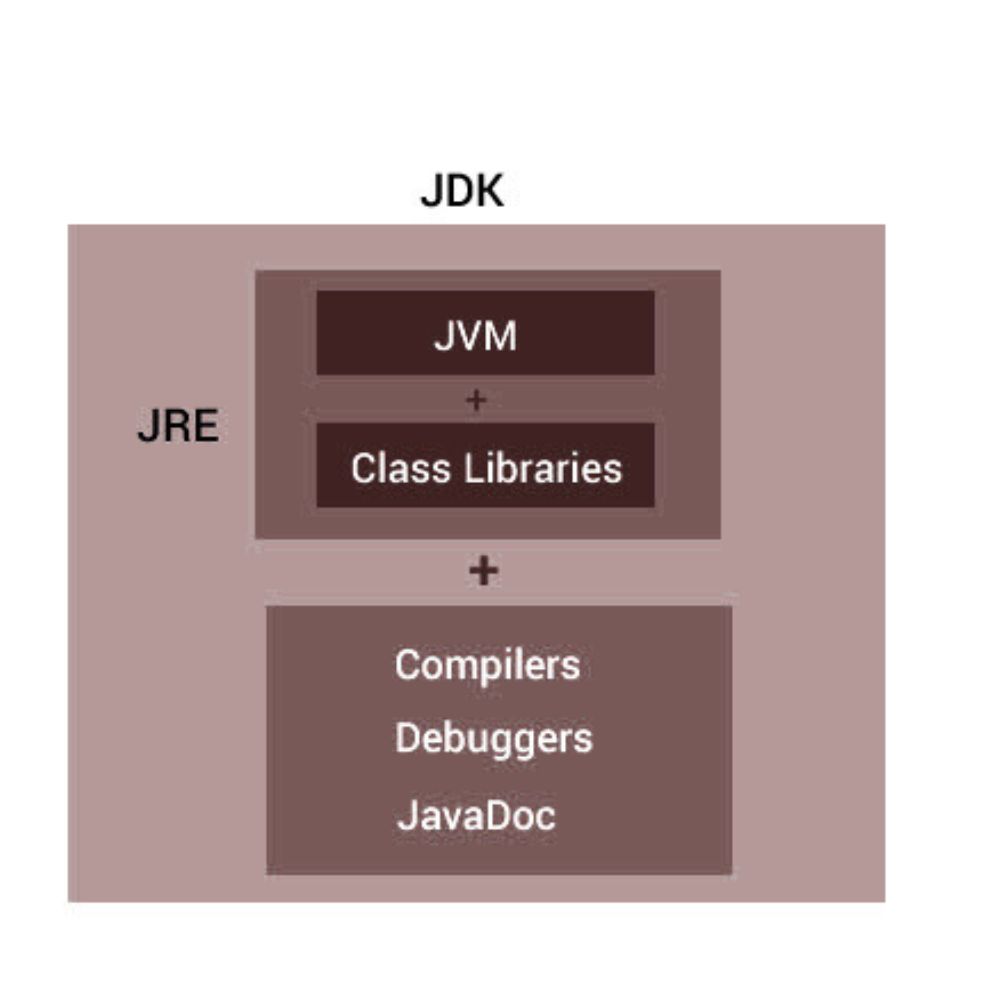
Difference between JDK , JRE and JVM :
| JDK | JRE | JVM |
|---|---|---|
| Java development kit is used to develop java applications. | Java runtime environment is used to run java application | Java virtual machine is used to execute java bytecode. |
| JDK includes JRE+Development tools (javac, debugger etc) | JRE includes JVM + Libraries | JVM includes Class loader , JIT Compiler , Garbage collector |
| JDK is platform dependent | JRE is platform dependent | JVM is OS-specific, but bytecode is platform-independent |
| JDK is used for writing and compiling java code | JRE is used for running a java application on a system | JVM is used to convert bytecode into native machine code |
